Can reverse osmosis systems work with hard water?
Reverse osmosis (RO) systems are popular in the field of water treatment for their ability to efficiently remove pollutants. It can effectively filter out most dissolved solids, heavy metals and other impurities in water. However, many people are concerned about an important question: Can reverse osmosis systems effectively treat hard water? Will hard water have adverse effects on reverse osmosis systems? This article will analyze this issue in detail.

What is the definition and harm of hard water?
Hard water refers to water containing high concentrations of alkaline earth metal ions such as calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺). These ions mainly come from the dissolution of calcium and magnesium minerals when water flows underground. According to its hardness, water can be divided into soft water, medium hard water, hard water and very hard water. Usually, the hardness of water is expressed in milligrams per liter (mg/L) or grains per gallon (gpg) of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) per liter of water.
Hard water has certain negative effects on daily life and industrial applications. For example:
1. Scale formation: Calcium and magnesium ions in hard water easily form scale in heating water pipes, water heaters, boilers and other equipment, reducing equipment efficiency and increasing energy consumption.
2. Affecting cleaning effect: Hard water reacts with soap and detergent to form insoluble precipitates, reducing cleaning effect and leaving traces that are difficult to clean.
3. Affecting the taste of water: Hard water may not taste as refreshing as soft water, and long-term drinking may also have health effects on some people.

How does the reverse osmosis system work?
The reverse osmosis system removes soluble solids and impurities in water through the selective osmosis of a semipermeable membrane. Its working principle is based on the concept of osmotic pressure. Water is forced to pass through a semipermeable membrane with a very small pore size by pressure. Impurities in the water are blocked on one side of the membrane, and pure water is collected through the membrane.
The pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is very small, about 0.0001 microns, so it can effectively filter out most ions, molecules and other impurities. Most dissolved solids (TDS), including hard water ions such as calcium and magnesium, can be effectively removed by the reverse osmosis system.
Can reverse osmosis effectively treat hard water?
Calcium and magnesium ions in hard water are one of the targets that the reverse osmosis system can filter. Due to the microporous structure of the reverse osmosis membrane, these ions cannot pass through the membrane, so most of the calcium and magnesium ions will be removed, thereby reducing the hardness of the water.
1. Effectiveness: The reverse osmosis system has a good treatment effect on hard water. It can significantly reduce the content of calcium and magnesium ions in water, and the hardness of the effluent water can usually be reduced to a very low level, close to the standard of soft water. Therefore, reverse osmosis technology is often used for hard water treatment, especially in application scenarios that require high-purity water, such as laboratories, pharmaceutical industries, and drinking water purification.
2. Outlet water quality: The water quality of hard water treated by the reverse osmosis system has been significantly improved. Not only calcium and magnesium ions in hard water are removed, but also other possible contaminants such as heavy metals, nitrates, chlorides and organic substances are removed.
What are the effects of hard water on the reverse osmosis system?
Although the reverse osmosis system can effectively treat hard water, hard water may have some adverse effects on the reverse osmosis system itself. One of the biggest challenges of the reverse osmosis system is the scaling problem. Calcium and magnesium ions in hard water easily combine with carbonate (CO₃²⁻), phosphate (PO₄³⁻) ions to form insoluble precipitates, which adhere to the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane, gradually block the membrane pores, and reduce the permeability and filtration efficiency of the system. Membrane scaling not only affects the flow rate and effluent quality of water, but may also cause premature failure of the membrane and increase maintenance costs.
Secondly, scaling caused by hard water will accelerate the aging and damage of the reverse osmosis membrane, thereby shortening the service life of the membrane. In order to extend the service life of the membrane, it is usually necessary to clean the membrane regularly or even replace it, which undoubtedly increases the operating cost and complexity of the system. In addition, the precipitates in hard water will increase the working pressure of the reverse osmosis system, thereby increasing energy consumption. This is because in order to overcome the scaling on the membrane surface, the system needs to apply greater pressure to ensure the normal penetration of water through the membrane.
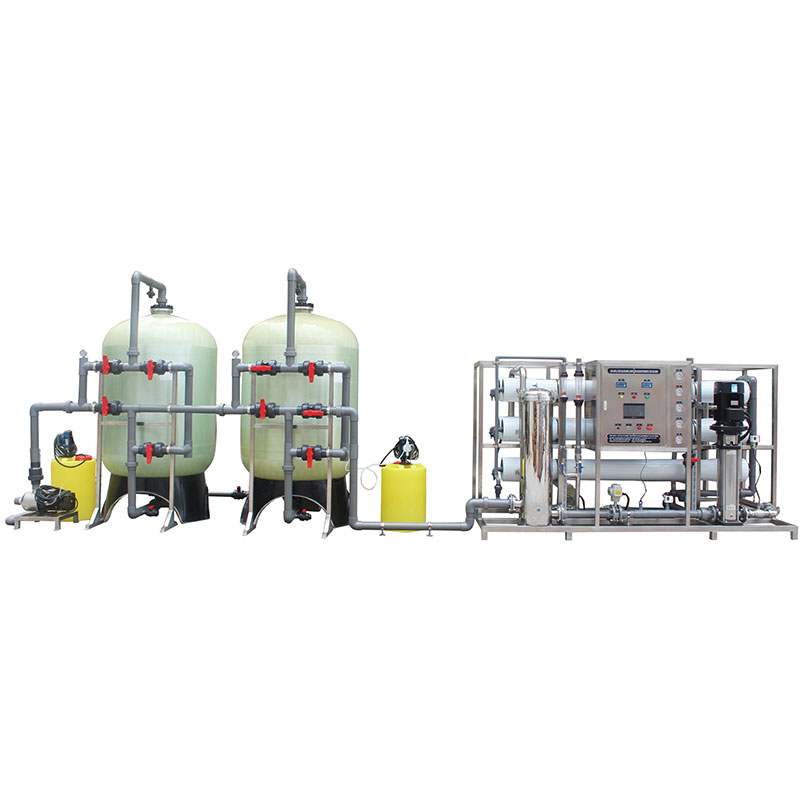

What are the measures to deal with the impact of hard water on the reverse osmosis system?
In order to prevent the adverse effects of hard water on the reverse osmosis system, a water softener or ion exchange system can be configured in front of the reverse osmosis system, which can effectively remove calcium and magnesium ions in hard water and prevent these ions from forming scale on the reverse osmosis membrane. The water softener replaces calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions through ion exchange resins, thereby reducing the hardness of the water.
Secondly, adding anti-scaling agents is a common method to prevent calcium and magnesium ions from forming precipitation on the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane. These chemicals inhibit the formation of precipitates by changing the crystal structure of ions, thereby extending the service life of the membrane.
Regular chemical cleaning of the reverse osmosis system can remove scale on the membrane and restore the permeability and filtration efficiency of the system. The cleaning process usually uses an acidic solution to dissolve and remove carbonate and phosphate precipitates on the membrane surface. In addition, choosing a reverse osmosis membrane with better scaling resistance can also reduce the impact of hard water on the system to a certain extent. Modern reverse osmosis membrane technology is constantly improving, and some membrane materials and structural designs can better resist scaling problems.
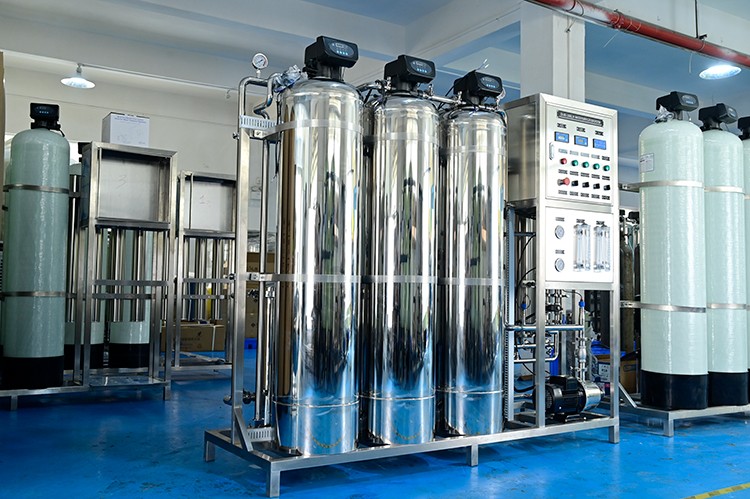

In general, the reverse osmosis system can effectively treat hard water, remove calcium and magnesium ions in water, and make the water quality purer. However, the problem of membrane scaling caused by hard water in reverse osmosis systems cannot be ignored. Membrane scaling not only reduces the efficiency of the system, but may also shorten the service life of the membrane, increase energy consumption and maintenance costs.
In order to maximize the performance of the reverse osmosis system and extend its service life, it is recommended to configure a water softener or use an anti-scaling agent at the front end of the system, combined with regular maintenance and cleaning measures to prevent the negative effects of hard water.